Join Tables
You can join multiple tables within the same query. The Query Builder automatically highlights tables related to any of the previously added tables. Drag-and-drop a subordinate table in the same way you added a main table to include it in a query and automatically create an inner join relation based on a key column.
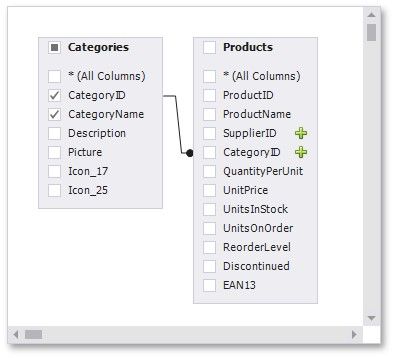
Alternatively, you can join tables by clicking the plus button ![]() in a row corresponding to a key column.
in a row corresponding to a key column.
You can customize the relationship by right-clicking it on the diagram and selecting Edit Relation in the invoked context menu. Use the Join Editor to select the join type (Left Outer or Inner), apply a logical operator (Equals to, Is less than, etc.) and column key fields.
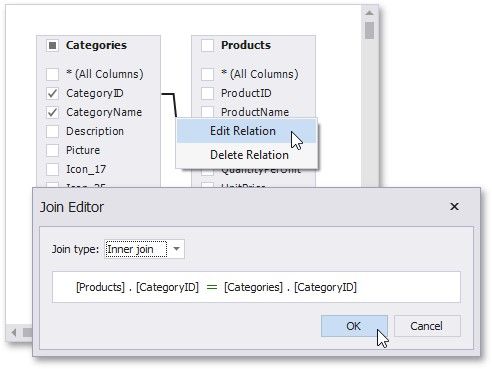
A left outer join returns an inner join’s values, along with all the values in the "left" table that do not match the "right" table, including rows with NULL (empty) values in the key field.
When the left outer join is selected, the relationship line displays an arrow pointing to the "right" table.
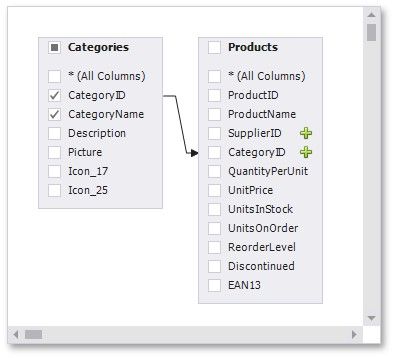
You can manually join tables if they do not have a relationship at the database level. In this case, when you drag-and-drop a table onto the list of tables, the Join Editor is automatically invoked allowing you to construct a custom join relationship.
After executing the query, it returns a "flat" table composed of data records selected based on the specified join options.
Note: Although joining different tables within a single query may be required in some scenarios, creating hierarchical data sources generally results in better performance (in general, master-detail reports are generated faster than similar-looking reports created by grouping "flat" data sources).